How are UI and UX different from each other?
Today, as you power up your laptop, tablet, or mobile phone and navigate to the Internet, every interaction is facilitated by a user interface (UI). Whether you logged into your browser, checked your email, or landed on this site to read this article, your seamless experience resulted from good user experience (UX) design. Yet, despite their intertwined roles, UX and UI are often conflated. This article aims to clarify their distinction, exploring the meaning of UX and UI, their collaborative nature, the requisite skills for UI/UX designers, and career prospects, including salaries and paths. But first, let’s establish some foundational definitions.
What is UI Design?
UI design or User Interface design often focuses on creating visually appealing and intuitive interfaces to facilitate user interaction with digital products or systems. It involves designing elements such as buttons, menus, icons, and layouts to enhance usability and accessibility. UI designers strive to optimize the user experience by ensuring the interface is aesthetically pleasing, easy to navigate and aligns with user expectations and preferences. Ultimately, UI design aims to make interactions seamless and enjoyable for users across various platforms and devices.
What is UX Design?
UX design, or User Experience design, encompasses the process of enhancing user satisfaction by improving the accessibility, usability, and overall interaction experience of a product or system. It involves understanding user behaviors, needs, and preferences through research and analysis, then designing intuitive interfaces and workflows that align with user goals. UX designers focus on creating seamless and meaningful experiences that foster positive emotions and effectively address user pain points, ultimately driving engagement and loyalty.
A UI UX course comprehensively understands User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) design aspects. These courses cover principles, methodologies, and tools essential for crafting visually appealing interfaces while prioritizing user satisfaction and functionality. By exploring topics such as usability testing, wireframing, prototyping, and design thinking, students gain insights into designing interfaces that look good and deliver seamless and intuitive user experiences. This holistic approach equips individuals with the skills to excel in UI/UX design.
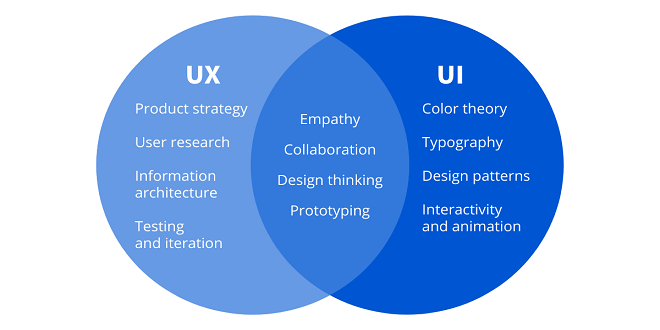
Now that you are familiar with the terms UI and UX let’s delve into understanding the difference between the two terms on the basis of aspects that are extensively used interchangeably.
Purpose
UI: User Interface (UI) design focuses on creating visually appealing and intuitive interfaces that enable users to interact with digital products effectively. It aims to enhance usability, accessibility, and aesthetic appeal by designing buttons, menus, and layouts. UI design also that the interface is visually appealing and easy to navigate, thereby improving user satisfaction and engagement.
UX: User Experience (UX) design aims to optimize users’ overall experience when interacting with a product or system. It aims to understand user needs, behaviors, and preferences through research and analysis, then design interfaces and workflows that align with user goals. UX design enhances usability, accessibility, and emotional satisfaction, fostering positive interactions and driving user engagement and loyalty.
Application
UI: User Interface (UI) design finds applications in various digital platforms and devices, including websites, mobile apps, software applications, and smart devices. It focuses on creating visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces that facilitate smooth interactions between users and products. UI design ensures that users can easily navigate through different features, access information efficiently, and perform tasks seamlessly, ultimately enhancing their overall experience with the digital product or system.
UX: User Experience (UX) design is applied across all stages of product development, from conceptualization to post-launch evaluation. Its primary goal is to create intuitive and enjoyable user experiences by understanding their needs, behaviors, and preferences. UX design involves conducting user research, creating wireframes and prototypes, testing usability, and iteratively refining the design based on user feedback. By prioritizing user satisfaction and engagement, UX design helps optimize the overall experience of interacting with digital products and services.
Focus
UI: User Interface (UI) design focuses on a digital product’s visual presentation and interaction elements. It concerns itself with creating intuitive layouts, attractive visual designs, and responsive components such as buttons and menus. UI design ensures users can easily navigate and interact with the product’s interface, enhancing usability and aesthetic appeal.
UX: User Experience (UX) design centers on users’ overall experience when interacting with a product. It involves understanding user behaviors, needs, and emotions to create seamless and satisfying interactions. UX design optimizes usability, accessibility, and emotional engagement, aiming to deliver a cohesive and enjoyable experience across the user journey.
Creation Process
UI: User Interface (UI) creation involves several steps, including understanding user requirements and business objectives. Designers then create wireframes and prototypes to visualize the layout and functionality of the interface. They select color schemes, typography, and visual elements to create an appealing design. Finally, UI designers collaborate with developers to implement the design and ensure its responsiveness and usability across different devices and platforms.
UX: User Experience (UX) creation begins with extensive research to understand user needs, behaviors, and pain points. Designers then develop user personas, user flows, and information architecture to guide the design process. Prototypes are created and tested iteratively with real users to gather feedback and refine the design. UX designers continuously evaluate and optimize the user experience to ensure it meets the desired objectives and delivers maximum value to users.
End Result
UI: The result of User Interface (UI) design is a visually appealing and user-friendly interface that facilitates seamless interaction between users and digital products. It encompasses intuitive layouts, visually appealing elements, and responsive components that enhance usability and aesthetic appeal, ultimately leading to a positive user experience.
UX: User Experience (UX) design aims to deliver a satisfying and meaningful user interaction when engaging with a product or service. The result is an optimized user journey that addresses user needs, preferences, and pain points, increasing satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty. Through research, iteration, and refinement, UX design ensures that the final product effectively meets user expectations and achieves its intended objectives.
Conclusion
While user Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) are closely related, they serve distinct purposes in the design process. UI focuses on a product’s visual presentation and interaction elements, while UX centers on the overall experience and satisfaction of users. Understanding these differences is crucial for designers to create successful digital products. Enrolling in a UI UX course equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate this dynamic industry. By learning both UI and UX principles, designers can effectively create interfaces that look great and provide seamless and meaningful experiences for users, driving success in the design field.




